From the alpine meadow to the eternal ice.
You can drive the scenic road on 365 days a year.
A natural spectacle created by the sculptural power of the glaciers
A ride along the Kaunertal Glacier Road opens up all the vegetation levels in the Alps. The journey from the valley to the mountains leads from lush green meadows up to the eternal ice. What can be experienced here at a very short distance can otherwise only be experienced on a trip from Northern Germany to Greenland.
 600 700 800 900
600 700 800 900 600 m to 900 m altitude
The Glockturm mountain protects the valley floor of the Kaunertal from cold north winds – the Colline step climbs well over 900 m on the warm southern slopes.
Average annual temperature:> 6 °
Vegetation: cultivated arable land, fruit trees, deciduous and mixed forests
 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600
1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1,000 m to 1,600 m altitude
Fruit growing and agriculture is still possible at this altitude on the warm south-facing slopes.
Average annual temperature: 3°
Vegetation:
Thick larches, pine forests, steep mountain meadows full of flowers
 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 2100
1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 2100 1,700 m 2,100 m altitude
The tree line in the Kaunertal lies at approx. 2,100 metres and is made up of Swiss pine, which can withstand temperatures to minus 40°.
Average annual temperature: 0°
Vegetation:
Swiss pine, light coniferous forests, and stunted trees such as the green alder and mountain pine.
 2100 2200 2300 2400 2500 2600 2700 2800
2100 2200 2300 2400 2500 2600 2700 2800 2,100 m to 2,800 m altitude
Alpine lawn with colourful alpine flowers and grasses. The Alpine flowers are particularly colourful as a result of more intense UV radiation on the mountain.
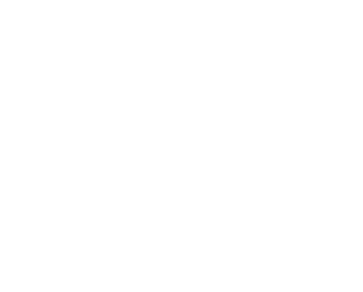
Average annual temperature: >-1° to -3°
Vegetation:
Edelweiss, spring gentian, mountain avens, primrose, small dianthus, glacier buttercup (requires 2-3 vegetation seasons before flowering).
 2800 2900 3000 3100
2800 2900 3000 3100 2,800 to 3,100 m altitude
Isolated plants with a short vegetation season and a sophisticated root system for optimum nutrient absorption, climatic snowline at approx. 3,100 m.
Average annual temperature: < -3°
Vegetation:
Mosses, clump-forming flowering plants and lichens, existing in a symbiosis between fungi and algae.
 3100 3200 3300 3400 3500
3100 3200 3300 3400 3500 over 3,100 m altitude
More snow falls on average than melts, forming a permanent cover of snow – glaciers.
Vegetation:
Higher plants no longer occur in the upper part of the nival zone. Only thallophytes exist, as they do not require a substratum of soil. They can be found growing densely on the surface of rocks that remain uncovered by ice.
 -3°C
-3°C

